Introduction:
Zirconium dioxide is also known as zirconia (ZrO2). This ceramic material has garnered significant attention in various industries due to its remarkable properties.

This article explores the features, uses, and future potential of zirconium dioxide. Hope that you can learn more about this material of the future.
Understanding Zirconium Dioxide:
Zirconium dioxide is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most notable attributes include high melting point, remarkable strength and toughness, excellent wear resistance, and outstanding thermal properties. These characteristics make it an ideal material for numerous advanced applications.
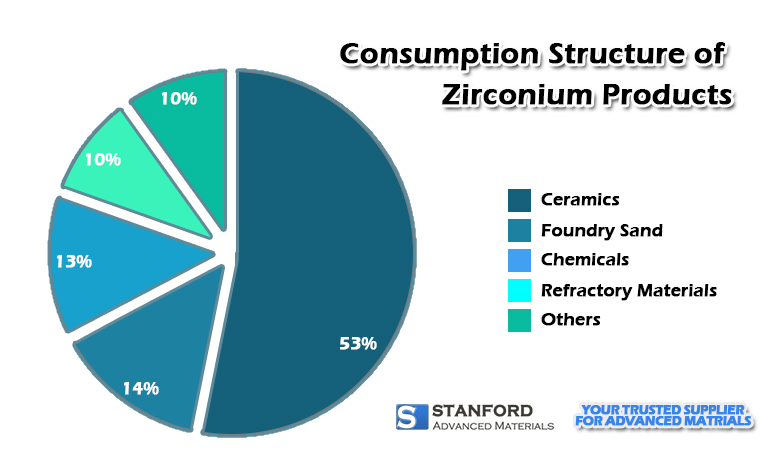
Related reading: Zirconium Dioxide Properties & Applications
Properties of Zirconium Dioxide:
This advanced material stands out for a unique set of characteristics. ZrO2 has become suitable for a wide range of applications. Its uses range from high-temperature industrial uses to critical roles in the medical field.
- High Strength and Toughness: It is notable for its exceptional mechanical strength and toughness. Its strength surpasses most other ceramic materials.
- Thermal Stability: It has a very high melting point of around 2700°C or 4900°F. Also, it is notable for excellent thermal stability. So, ZrO2 is suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Wear Resistance: Zirconium dioxide exhibits a high degree of hardness and chemical inertness. These two features greatly contribute to its exceptional wear and corrosion resistance. Thus, it has become an ideal material for applications requiring durability and longevity.
- Biocompatibility: Zirconium dioxide is biocompatible. It is safe for use in medical implants.
Applications of Zirconium Dioxide:
Zirconium dioxide has widespread applications. Its uses involve the medical field to industrial, automotive, aerospace, and electronic sectors. This broad utility is a testament to zirconia’s effectiveness in meeting specific demands across different domains.
- Dental and Medical Industry: Zirconia finds common use in dentistry due to its tooth-like color and strength. You can also find it in orthopedic implants and other medical prosthetics.
- Industrial Uses: In the industrial sector, zirconia is useful for manufacturing cutting tools, grinding media, etc. It also serves as an additive in refractory materials due to its high-temperature resistance.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Zirconium dioxide finds applications in these industries for thermal barrier coatings on engine components. It provides protection against high temperatures.
- Optical and Electronic Applications: Its optical properties find use in fiber optics and other electronic devices.
Innovations and Future Potential:
Zirconium dioxide (zirconia) possesses a dynamic nature and adaptable properties. So, it is a focal point for continuous research and development.
1. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs):
- One of the significant innovations is solid oxide fuel cells. Here, zirconium dioxide acts as an electrolyte.
- SOFCs with zirconia are notable for their efficiency in energy generation. They offer a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.
- ZrO2 has high-temperature stability. Thus, it is particularly suitable for this application. ZrO2 enables SOFCs to operate at high efficiencies.
2. Environmental Applications:
- Zirconia is useful in environmental applications, particularly in catalysis for pollution control.
- Its properties are advantageous in catalytic converters. These converters reduce harmful emissions from vehicles and industrial processes.
- This material has the ability to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion. It is ideal for long-term use in harsh environmental conditions.
3. Future Potential:
- The ongoing research is uncovering new potential uses for zirconium dioxide. Its unique properties open doors to a range of future applications.
- The material’s role in green technologies and sustainable processes is particularly promising. There are great global efforts to combat climate change and reduce environmental impact.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite its advantages, the processing and machining of zirconium dioxide can be challenging and costly. That’s because ZrO2 is extremely hard. Future research focuses on overcoming these challenges and expanding its applications, particularly in sustainable energy and environmental technologies.
Conclusion:
Zirconium dioxide stands out for its unique blend of properties and various applications. From healthcare to high-tech industries, its role is rapidly expanding. That paves the way for innovations that could redefine the use of ceramics in the modern world. As research progresses, the potential of zirconium dioxide continues to grow.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) boasts extensive expertise in the production and provision of top-quality zirconium dioxide products. A variety of Zr products are available on our website. For more information, please do not hesitate to reach us.