Zirconium, chemical symbol Zr, atomic number 40, melting point 1852°C, is one of the high melting point metals. Zirconium with special excellent properties, such as the resistance to high temperature, oxidation, corrosion, and abrasion, all of which made it a wide range of applications as the structured and functional ceramic material in many industrial sectors, especially in the high-tech industry.
Zirconium products and their applications
- Zirconium silicate
Zirconium silicate is an important kind of traditional zirconium product. Products can be prepared with zircon sand as raw material, after grinding, calcination, and powder, is a kind of high-quality and inexpensive ceramic glaze opacifying agent, mainly used in ceramics and porcelain, building ceramics color glaze production, has been widely used in high-grade refractory materials, precision casting, emulsified glass and other industries.

- Zirconium carbonate
Zirconium carbonate is mainly used as cosmetic additives and waterproof agents, flame retardants, sunscreen, fiber and paper surface additives, and can be used for preparing zirconium cerium catalytic composite material, is an important raw material for textile, papermaking, paint, cosmetics industry, the amount of growth in recent years.
- Zirconium oxychloride
It can be used for other zirconium products such as two – zirconium oxide, zirconium carbonate, zirconium sulfate, zirconium and hafnium compound preparation and separation of zirconium and hafnium metal material, can also be used for textile, leather, rubber additives, metal surface treatment agent, coating driers, refractories, ceramics, catalyst, fire retardant, and other products.
- Fused zirconia
Fused zirconia is mainly used in the production of glazes and refractories. Due to the high content of impurities in the fused zirconia, the use is limited.
- Zirconium sulfate
It is the important raw material in the production of leather tanning agent, wool processing agent and paint surface oxidation agent, can be used as a catalyst carrier, amino acid, and protein, precipitant, and deodorant, intermediate raw materials are for zirconium chemicals and metal zirconium and hafnium.
- Zirconium oxide
The white solid, non-toxic, tasteless, has enough stability of alkali solution and many acidic solutions, suitable for precision ceramics, electronic ceramics, optical lenses, glass additives, dissolving zirconia brick, ceramic pigment, glaze, artificial stone, refractory materials, grinding and polishing industry and products.
It is also known as semi-stable, stable zirconia is a white powder with non-toxic, tasteless, and stable chemical properties, the specific surface area is controllable, manufacturing all kinds of special ceramics, advanced refractories, new energy materials, optical communication devices, based on raw materials.
- Zirconia structural ceramics
Using the composite zirconium oxide as the raw material, including two kinds of products such as zirconia grinding and zirconia structure, the structure of zirconia mainly includes the zirconia special ceramic valves, fiber optic connectors, ceramic knives, watches accessories, ceramic scissors, textile porcelain, etc.
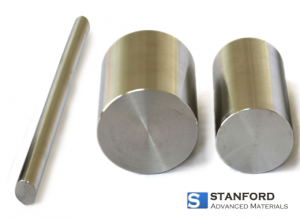
Since Zirconium has very good chemical corrosion resistance, zirconium shapes, such as zirconium tubes and zirconium rods are used to make equipment for the chemical industry.
- Nuclear grade zirconium
It is an important strategic metal used primarily for nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, nuclear submarines, and civilian power reactors, as well as the cladding of uranium fuel elements.
- Industrial grade zirconium
It is mainly used for the production of industrial-grade zirconium – chemical corrosion resistance equipment, military industry, electronic industry, pipeline valve materials, special high strength and high-temperature alloy materials, electric vacuum, and lighting industry getter.
- Firearm zirconium
It is also used in the combustion of the flame zirconium sponge, and also can be used in alloy additives and metallurgical deoxidizers, chemical industry, civil flash fireworks and so on.
Please visit http://www.samaterials.com for more information.