Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) is a kind of metal oxide material with many excellent properties such as high melting point (2700 ℃) and high boiling point, small coefficient of thermal conductivity, thermal expansion coefficient, high-temperature resistance, good wear resistance, corrosion resistance. Nano zirconia powders have many important applications because of their nanometer properties. Fine ceramics made of nano zirconia have some special properties under different conditions, such as insulator at room temperature, conductivity, sensitivity, and toughness at high temperature.
In the zirconium industry chain, the most widely used composite zirconia is the stable/partially stable zirconia formed by doping the corresponding rare earth elements according to different uses. The variety and content of the added rare earth elements can be adjusted to produce composite zirconia that meets the requirements of different uses, such as yttrium stabilized zirconia used as structural parts and zirconium and cerium eutectic used as catalysts. Compared with common zirconia, nano-scale composite zirconia has a smaller particle size and reaches the nanometer level. Its higher additional use value and the market scale of over ten billion are being rapidly developed.
Here are 10 applications of nanocomposite zirconia.
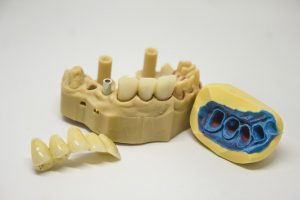
Denture material
Nano ZrO2 can obviously improve the room temperature strength and stress strength factor of ceramics, thus doubling the toughness of ceramics. The composite bioceramics prepared with nanometer ZrO2 have good mechanical properties, chemical stability, and biocompatibility. It is a promising composite bioceramics material, especially in the field of dental materials and artificial joints. Biomaterials refer to materials with natural organ tissue function or partial function, and they are the latest branch of biomedical science and have broad application prospects. Bioceramics have been widely used in the field of oral prosthodontics because of their excellent biocompatibility, stability, and aesthetics.
Zirconia toughened ceramic, as a new fine ceramic, has good mechanical properties (fracture toughness, strength, hardness, etc.), biocompatibility and stability, aesthetics, thermal conductivity, and formability, which can well solve the problem of insufficient strength and toughness of conventional all-ceramic crown materials. Secondly, as an excellent bioinert ceramic, it has excellent chemical stability both as an oral prosthesis and an implant, which fully meets the standard as an oral prosthesis material.
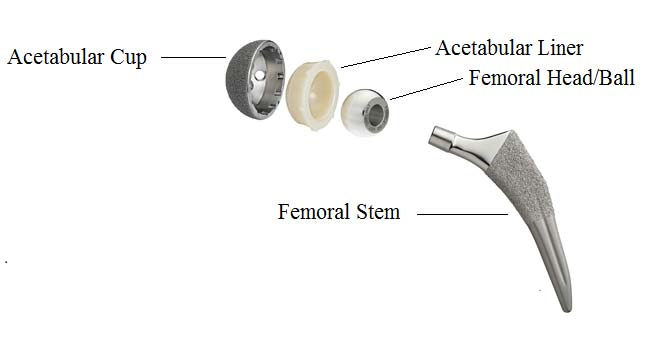
Joint prosthesis
The initial ceramic artificial joint is not perfect and has undergone four generations of process improvement so far, gradually becoming perfect. The fourth generation of the artificial ceramic joint is composed of several kinds of oxidized crystal materials such as zirconia, with good toughness and strength its performance is much better than that of the third generation of the ceramic joint. When zirconia is compounded, the crystal particles become smaller. More importantly, zirconia disperses and absorbs the energy of the fracture, inhibiting crack growth. Zirconia is the best prosthesis material currently used in clinical hip replacement, the ceramic material with the best wear resistance is the most ideal especially for middle-aged and young patients with high exercise.
Oxygen sensor
The sensor made of zirconia has good electrical conductivity, which plays an important role in controlling automobile exhaust and boiler combustion in power plants. In the automotive industry, oxygen sensors are essential for the use of three-way catalytic converters in engines to reduce emissions and pollution. The Zirconia oxygen sensor is one of the most mature oxygen sensors with the largest output. It is one of the key components of the automobile emission control system, and its signal output characteristics directly affect the engine fuel economy and emission control.
The catalyst for automobile exhaust purification
The catalyst for automobile exhaust purification: carrier (alumina), co-catalyst (nano-coating to increase the specific surface area, as a hydrogen storage material), catalyst (general gasoline parking space platinum, palladium, rhodium, etc., diesel vehicles for vanadium, tungsten, titanium, etc.). Zirconium-cerium solid solution composite oxide is used as a cocatalyst and important coating material. In addition, zirconium-cerium solid solution is also widely used in sensor materials, polishing materials, fuel cells, structural materials, high-strength ceramics, and other fields.
Catalysts for chemical synthesis of aromatic hydrocarbons
Zirconia has long been used in the study of isomeric synthesis. Isomeric synthesis is a process in which syngas is converted into isobutene and isobutane (i-C4) in high selectivity, and it is mainly composed of metal oxides such as zirconia, thorium oxide and cerium oxide. Since Pichler et al. studied isomeric synthesis for the first time, zirconia has become the core of isomeric synthesis catalysis research due to its high i-C4 selectivity and non-radioactivity. This highly selective formation of i-C4 has been attributed to the fact that zirconia surfaces are both acidic, alkaline, oxidizing and reductive. If a single zirconia catalyst can convert syngas into aromatics or high-octane products in one step, the problem of mismatching of active centers in the catalytic system doped by metal and molecular sieve can be avoided, which has far-reaching significance for future energy development.
Ceramic core for fiber optic connector
Due to the excellent mechanical properties, chemical stability and extremely high precision of nano-yttrium oxide stabilize zirconia (nano-YSZ) powders, it can be used to prepare rare earth structure ceramic fiber core (precision needle) and sleeve for optical fiber connectors. It is the optical fiber passive device with the widest application range and the largest demand in the optical fiber network and is an important part of the information network infrastructure construction.

Mobile terminal products
As 5G, wireless charging and other new transmission methods approach, wireless frequency band becomes more and more complex, and metal case shielding will become a major bottleneck. The strict layout of 5G antenna requires the transformation of the existing metal housing material, and both ceramic and glass will be optional. Metal is also unfriendly to wireless charging. Most of the previous wireless charging technologies used electromagnetic wave raw materials, and metal would cause interference to the electromagnetic wave, which greatly reduced the charging efficiency. There are alternative materials such as plastics, glass, and ceramics. Plastic surfaces are prone to scratches, while glass is brittle, so ceramic materials, with their excellent physical properties, are gradually penetrating the appearance of smartphones.
The mi MIX is equipped with an all-ceramic body, and the microcrystalline zirconium ceramics, second only to sapphire hardness, is selected as the blank. It has a Mohs hardness of 8.5. Keys, knives and so on do not cause any wear and tear.

In fingerprint unlock applications, zirconia’s dielectric constant is three times that of sapphire, making the signal more sensitive. Compared with the 0.3mm sapphire cover plate used in iPhone Touch ID, the zirconia has higher recognition when the same thickness is used. It is expected that fingerprint recognition will become the standard of smartphones in the next 5-10 years.
Zirconia ceramic crucible
In the smelting of rare and refractory precious metals and alloys, the general materials are difficult to meet the requirements due to the need to heat to a higher temperature. Crucible made of zirconium oxide can be heated to 2430 ℃, the zirconium oxide thus become the first choice under the condition of high-temperature crucible pot zirconia materials.
Zirconia ceramic cutter
Ceramic cutters were used in the early 20th century, but their brittleness limited their range of use. However, its toughness has been greatly improved with the development of nanocomposite zirconia composite in recent years. Zirconia can be processed into various cutting tools, while the zirconia ceramic blades are made of special ceramic materials belonging to non-metallic materials. Zirconia ceramic tool not only has the advantages of traditional metal tools but also has the characteristics of no rust, health, wear resistance and so on, so it is known as ceramic steel.
Refractory material
Zirconia is often used as a refractory due to its high melting point, low thermal conductivity, and stable chemical properties. The advantages of refractory materials prepared with nano zirconia are more obvious, such as high-temperature resistance, high strength, good thermal insulation performance, and excellent chemical stability.
Please visit http://www.samaterials.com for more information.